

This equation determines the rate of fluid across the capillary membrane (Jv) and takes the difference between the hydrostatic pressures of the capillary fluid (Pc) and the interstitial fluid (Pi), as well as the oncotic pressure of the capillary fluid (Op) and the interstitial fluid (Oi). Combining these two components yields the Starling equation: Jv = Kfc - n (Op-Oi)]. Several different factors mediate the redistribution of water between the two ECF compartments: hydrostatic pressure, oncotic pressure, and the osmotic force of the fluid. To manage these two parameters, body water will redistribute itself to maintain a steady-state so that the osmolarity of all bodily fluid compartments is identical to total body osmolarity. To understand the different principles, it is essential to realize the following: ingestion and excretion of water and electrolytes are under tight regulation to maintain consistent total body water (TBW) and total body osmolarity (TBO). Several principles control the distribution of water between the various fluid compartments.
#Renal physiology practice questions body fluid compartments how to#
This article will primarily cover the physiologic composition of water in the human body, differentiate the various compartments in the body and their associated volumes and compositions, depict how to measure the different volumes, and delve into the clinical relevance associated with disturbances of the normal physiological conditions.
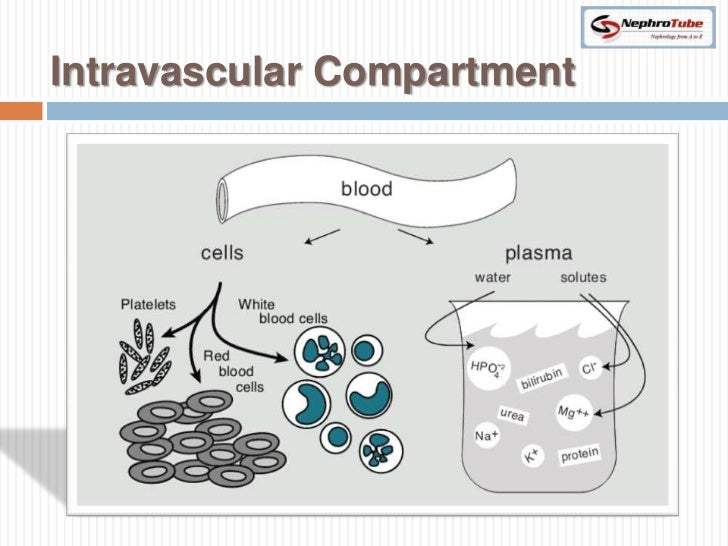
However, various clinical pathologies can alter the fluid composition and its constituents in the multiple compartments of the human body, which can have deleterious effects on our health and often require intensive interventions to monitor and maintain normal physiological conditions. As the distribution of the fluid in the body and the substances found within is critical for the maintenance of intracellular and extracellular functions pivotal to survival, the body has developed mechanisms to control compartment composition tightly. Examples of proteins include coagulation factors, immunoglobulins, albumin, and various hormones. A third important group of substances contained within the water of our body, which includes proteins, most of which are vital for our existence.

Another group includes metabolites, such as oxygen, carbon dioxide, glucose, urea, etc. One such group of substances includes electrolytes such as sodium, potassium, magnesium, phosphate, chloride, etc. The fluids of the body are primarily composed of water, which in turn contains a multitude of substances.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
